Education is a powerful driver of community development, influencing economic prosperity, social well-being, and individual success. Leveraging data from the 2022 American Community Survey 5-year estimates, we delve into the educational landscape of the United States, focusing on three crucial levels of education: High School Diploma or Higher, Bachelor’s Degree or Higher, and Graduate or Professional Degree.
High School Diploma Attainment or Higher
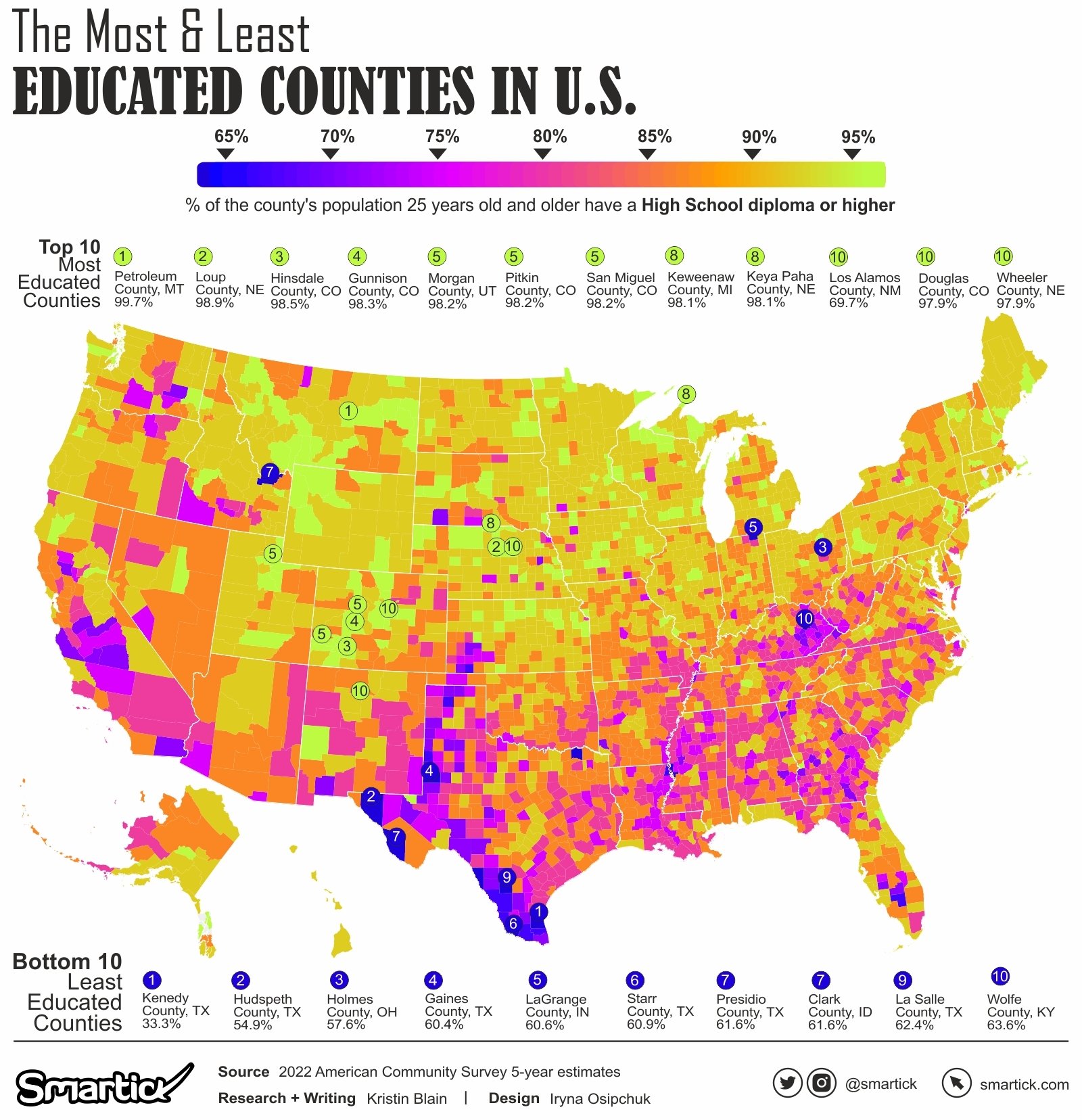
In the pursuit of a well-rounded education, certain counties stand out for their exceptional rates of high school diploma attainment. Topping the list are Petroleum County, Montana, and Loup County, Nebraska, boasting rates of 99.7% and 98.9%, respectively. On the flip side, counties such as Wolfe County, Kentucky, and La Salle County, Texas, face educational challenges with rates as low as 54.9%.
Visualizations vividly portray the geographic distribution of these counties, shedding light on potential influencing factors and prompting questions about educational equity.
Bachelor’s Degree Attainment or Higher
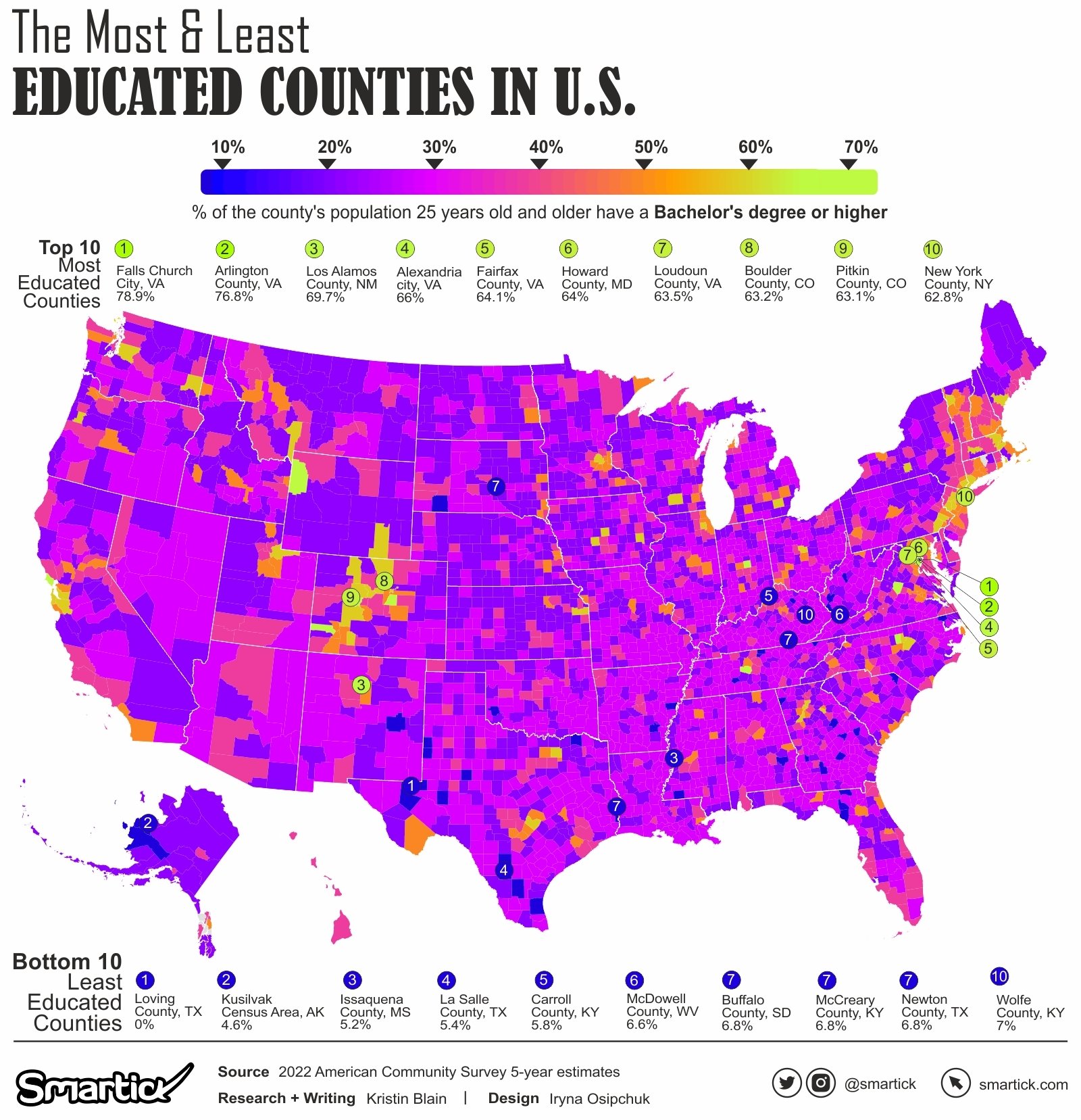
Moving up the educational ladder, some counties exhibit impressive rates of higher education attainment. Falls Church city, Virginia, claims the top spot with 78.9% of individuals holding a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher. In contrast, Wolfe County, Kentucky, struggles with only 4.7% of its population achieving this milestone.
Analyzing the patterns reveals intriguing correlations between educational attainment and socio-economic factors, sparking discussions on the potential impact of education on local economies.
Graduate or Professional Degree Attainment
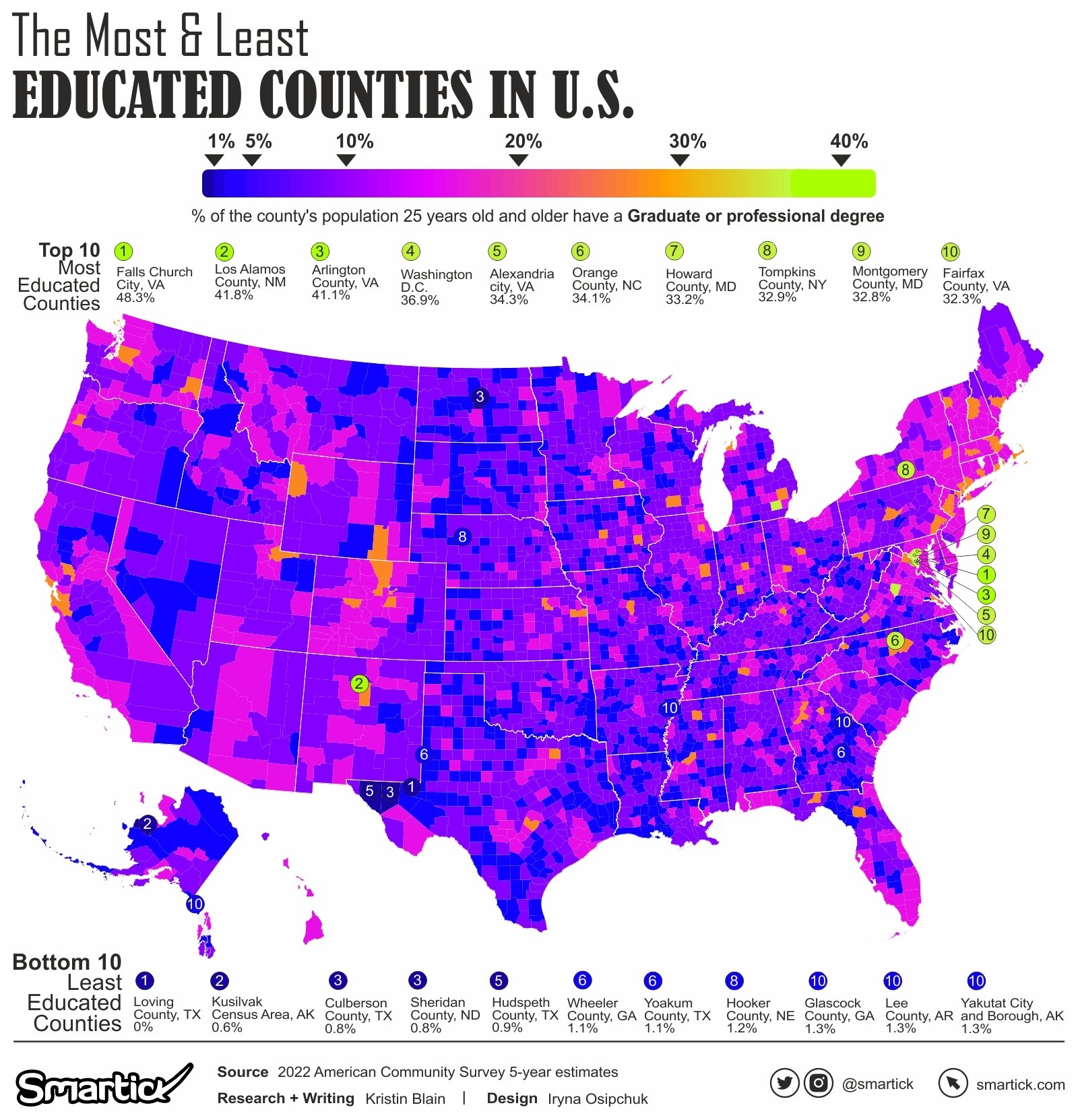
For those pursuing advanced degrees, Falls Church city, Virginia, remains at the forefront with an impressive 48.3% holding Graduate or Professional Degrees. However, a closer look at the bottom of the list reveals striking disparities, with counties like Yakutat City and Borough, Alaska, and Loving County, Texas, reporting percentages as low as 0%.
Through compelling visualizations, we gain insights into the geographic concentration of advanced degree holders, inviting further exploration into the role of education in shaping communities.
Key Findings and Trends
Across all three education levels, certain trends emerge. Counties in Virginia and Colorado consistently rank high, suggesting a correlation between geographic location and educational achievement. Conversely, some counties in Texas and Kentucky consistently struggle, indicating persistent educational challenges that demand attention.
Anomalies in the data prompt critical questions about the underlying factors influencing educational outcomes, paving the way for future research and policy considerations.
Implications and Insights
The educational disparities uncovered in this analysis have significant implications for local policymakers, educators, and community leaders. Addressing these gaps is essential for fostering inclusive development and ensuring equal opportunities for all residents.
This exploration of America’s educational landscape not only serves as a snapshot of the current state but also encourages ongoing efforts to understand and overcome challenges in education.
As we navigate the diverse educational terrain of the United States, it becomes clear that education is not only a personal achievement but a crucial determinant of community success. By shedding light on the most and least educated counties, we aim to inspire conversations, policies, and actions that pave the way for a more equitable and prosperous future.